Compared with other materials, composite materials have the characteristics of light weight, high strength, high temperature resistance, and corrosion resistance. Whether it is in the automotive field or the aerospace field, composite materials are ideal materials for the aerospace field.
With the gradual increase in the proportion of carbon fiber composite materials used in aircraft, the size of carbon fiber composite material accessories also increases. How to correctly select and rationally use cutting tools for high-efficiency and high-quality cutting is a very important issue.
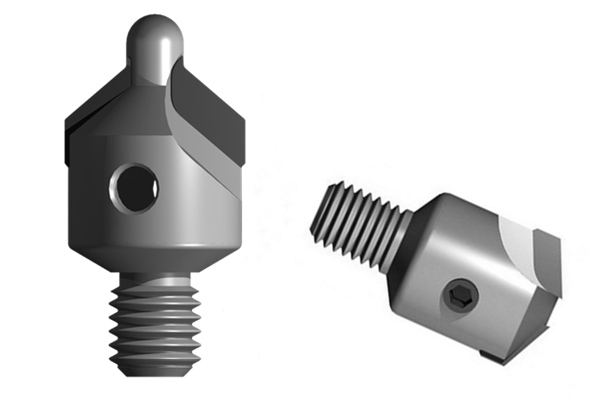
PCD countersink drill is suitable for processing CFRP, GFRP, titanium alloy and ceramic materials. The PCD cutting edge is sharper, the service life is long and the surface roughness is kept the best.
At present, the composite materials widely used in the aerospace field mainly include resin matrix composites, metal matrix composites, carbon matrix composites and ceramic matrix composites. For different composite material processing workpieces, the tool configuration solutions provided by Moresuperhard for customers are also Constantly update and improve to help customers improve the economic benefits of processing more effectively.
Difficulties in processing composite materials?
A: The material is highly abrasive, which causes a high wear rate of the tool;
The material is anisotropic, and the interlayer strength is low. Defects such as delamination and tearing are prone to occur under the action of cutting force during cutting, especially when drilling;
Due to the high cutting temperature, the thermal expansion coefficient difference between the reinforcing fiber and the matrix resin is too large, the dimensional accuracy and surface roughness of the machined surface are not easy to meet the requirements, and residual stress is easy to occur.
Processing carbon fiber materials with polycrystalline diamond pcd tools can greatly improve the surface quality of carbon fiber composite materials and improve production efficiency. It is an ideal tool.
PCD tool processing features:
PCD tools have sharp and wear-resistant cutting edges, which are very effective in processing composite materials such as carbon fiber reinforced materials (CFRP), glass fiber reinforced materials (GFRP) and aluminum-based silicon carbide (SiCp/AI), which are widely used in the aerospace field. Solve the defects of material delamination, tearing, burr and so on in the process of composite material processing
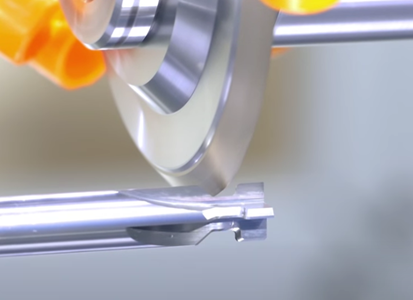
While obtaining precise and smooth cutting effect, it makes the processing efficiency higher, the wear resistance is better, and the tool life is longer. For example, drilling, hole processing is a common and important process in the processing of composite materials, especially carbon fiber, while carbon fiber parts used in aerospace can use PCD countersink drilling to process the edges of holes such as countersink holes, rivet holes and bolt holes. Using diamond PCD countersink drill, the sharp edge can ensure the good quality of the hole, smooth and burr-free.
What is spot facing? What kinds of countersinks are commonly used?
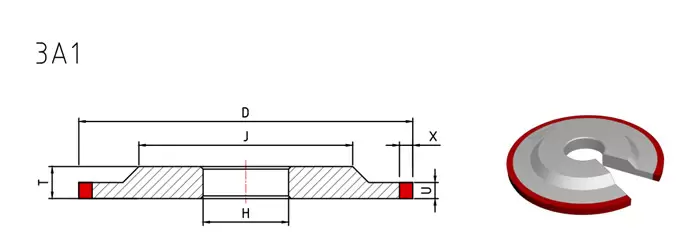
The surface of the orifice is processed with a countersinking method to process a flat-bottomed or tapered countersunk hole, which is called a countersink, and the countersink works as shown in the figure.
Countersinks are divided into cylindrical countersinks, tapered countersinks, and end countersinks:
1. Cylindrical countersinking is used for countersinking cylindrical countersinks.
The main cutting function of the cylindrical countersink is the end face blade, and the oblique angle of the spiral groove is its rake angle. There is a guide post at the front end of the countersink drill, and the diameter of the guide post is closely matched with the existing hole of the workpiece to ensure good centering and guidance. This guide post is detachable, and the guide post and countersink can also be integrated into one. (Generally, it is a countersunk knife, stepping on a cylindrical countersunk).
2. Tapered countersink is used for countersinking tapered holes.
The taper angle of the tapered countersink is different according to the requirements of the tapered countersink of the workpiece, including 60°, 75°, 82°, 90°, 100°, 120°, etc. Among them, 90° is used the most.
3. The end face countersinking drill is specially used for countersinking the end face of the hole.
Countersinking on the end face can ensure the perpendicularity of the end face of the hole to the center line of the hole. When the diameter of the machined hole is small, in order to maintain a certain strength of the tool bar, a section of the diameter of the tool bar head can be matched with the machined hole as a gap to ensure a good guiding effect.
What is reverse spot facing?
In the processing of some parts, it is necessary to spot-face the oblique or curved surface of the part to install bolts in the subsequent assembly, but due to the structural limitations of the parts, some spot-sinks cannot be spot-spotted from the front, and need to be reverse-sinked through the mounting holes of the bolts out, we call it reverse spot facing.
The role of countersinking?
Countersinking is the processing of planes, cylinders, tapers and other surfaces on the end face of the hole. Countersinking is used when machining cylindrical countersinks, tapered countersinks and end bosses on the machined holes.
Flat-bottom counterbore (English name Counterbore), its circumference and end face each have 3~4 cutter teeth, insert guide post into the processed hole, its function is to control the coaxiality error between the counterbore and the original hole . The guide post is generally made detachable, so as to facilitate the manufacture of the face teeth of the countersink drill and the sharpening of the countersink drill.
Flat-bottomed countersinking drill has 3~4 cutter teeth on its circumference and end face respectively, inserting a guide post into the processed hole, its function is to control the coaxiality error between the countersinked hole and the original hole. The guide post is generally made detachable, so as to facilitate the manufacture of the face teeth of the countersink drill and the sharpening of the countersink drill.
Compared with other materials, composite materials have the characteristics of light weight, high strength, high temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, etc., and become ideal materials in the aerospace field. With the wide application of aerospace composite materials, how to correctly select and rationally use cutting tools for efficient and high-quality cutting is a very important issue. At present, the tool materials widely used in the aerospace manufacturing industry mainly include cemented carbide, superhard tool materials and ceramics, among which cemented carbide and superhard tool materials account for the largest proportion. The leading tool in the development of aerospace industry tools has a wide range of applications.
Moresuperhard PCD superhard material cutting tools and carbide cutting tools have been maturely used in the field of aerospace manufacturing and processing. PCD tools and cemented carbide tools have finely ground sharp cutting edges, which are widely used in the aerospace field for composite materials such as carbon fiber reinforced materials (CFRP), glass fiber reinforced materials (GFRP) and aluminum-based silicon carbide (SiCp/AI) The effect is excellent, which effectively solves the defects of material delamination, tearing, burrs and so on in the process of composite material processing. While obtaining precise and smooth cutting effect, it makes the processing efficiency higher, the wear resistance better and the tool life longer. longer.
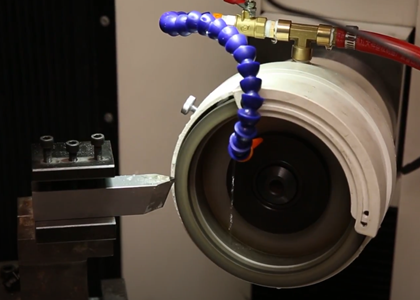
Hole machining and edge milling of parts are difficult points in the machining of aerospace composite materials. Therefore, Moresuperhard has developed high-performance hole machining tools and milling cutters made of PCD and cemented carbide, which are now mature. It is widely used in the processing of aerospace composite materials.
Drilling is a common and important process in the processing of composite materials, especially carbon fiber. Hole machining in composite materials is extremely prone to defects such as material burns, poor hole machining surface quality, delamination, tearing and collapse. The 8-edge twist drill in the Moresuperhard hole processing tool, the 8-edge design, reduces the cutting force when the drill is pulled away from the material, and avoids delamination; the tapered drill has a special drill tip shape, and the drilling axial force is small and the edge is small. The sharp edge ensures the good quality of the hole; PCD countersink drill, PCD cutting edge has high durability, good surface roughness index retention, precision grade 2A thread and taper surface fit, ensuring high precision, quick and easy replacement of the drill bit, 100° and The metric and American standard tools with 130° countersinking angle are supplied in full specifications; the drill-reamer-sinking integrated tool can complete drilling and countersinking at one time, omitting the need for retracting, changing and cutting tools when machining with conventional drills and reamers Indexing can greatly shorten the processing time, and the polishing margin can squeeze the hole wall.
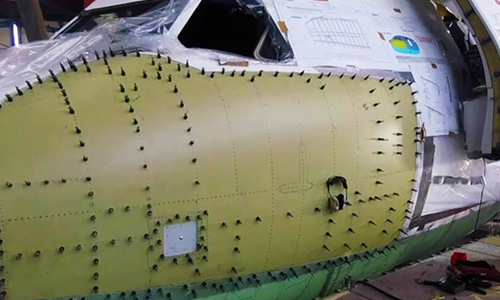
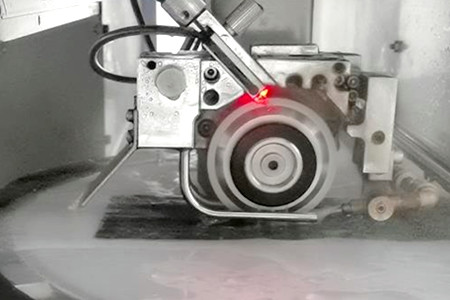
Case of turning Aircraft carbon fiber skin with PCD countersink drill
For carbon fiber skins, the rivet holes require high precision and are difficult to process, so PCD countersinking is generally used for processing.
Aircraft skin refers to the three-dimensional component that surrounds the frame structure of the aircraft and is fixed on the frame with adhesives or rivets to form the aerodynamic shape of the aircraft. The skin structure composed of aircraft skin and skeleton has a large bearing capacity and rigidity, but its own weight is very light, and it plays the role of bearing and transmitting aerodynamic loads. After the skin is subjected to aerodynamic action, the force is transmitted to the connected fuselage and wing frame. The force is complex, and the skin is in direct contact with the outside world. Therefore, not only the skin material is required to have high strength and good plasticity, but also a smooth surface. It has high corrosion resistance.