Grinding is a machining method for machining parts with high dimensional tolerances, which cannot be achieved by turning and milling methods.
Grinding is preferred for:
• Hard materials with good machining properties.
• High dimensional accuracy and high shape accuracy (IT5~IT6).
• Very small surface waviness and roughness (Rz= 1~3um).
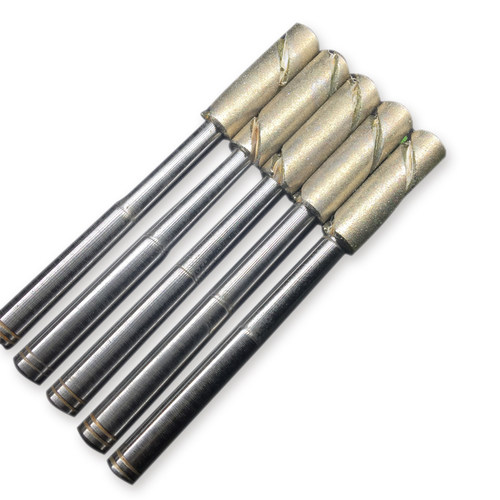
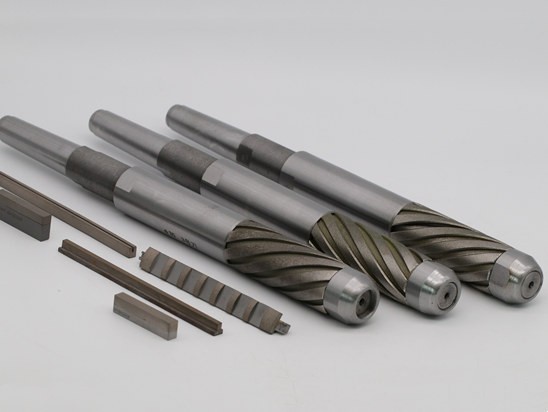
Abrasive tool
The rotating abrasive tool consists of abrasive particles, adhesive and closed pores. Most of the different shapes and positions of abrasive particles constitute negative cutting angles, and the cutting thickness of each abrasive particle is not always the same. Grinding is cutting with cutting edges of uncertain geometry.
Abrasive
Most grinding wheels contain abrasive particles composed of either natural corundum (white, pink) or silicon carbide (green, black). The toughness of abrasive decreases with the increase of abrasive hardness. The brittle and hard abrasive particles have self-sharpening property due to the fragmentation of the abrasive particles when the abrasive load is small (fine grinding). Sufficient toughness can prevent premature fragmentation of the abrasive particles under heavy load (coarse grinding). The abrasive particles should have high hardness and sufficient particle toughness and heat resistance.
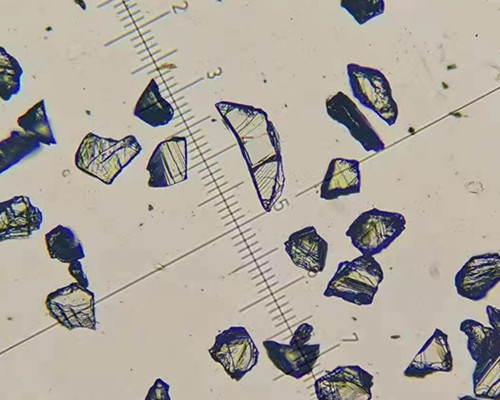

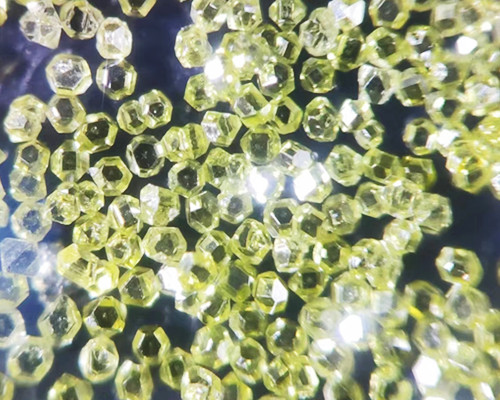
Abrasive wear
When the cutting force is high, the abrasive particles are broken and come out of the binder. When the cutting force is small, the abrasive load increases with the increase of friction and wear on the cutting edge, and finally the abrasive particles break into particles. A new cutting edge is formed by the fragmentation of the abrasive particles and the breaking out of the binder, and the grinding tool is self-sharpened by this process.
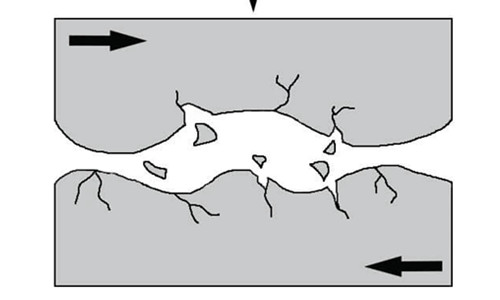
Abrasive types
Sharp abrasive particles are suitable for long chip materials. When grinding brittle materials, square grits have more wear resistance, and single grain grits (single grain crystals) have very high grain strength, so they are especially suitable for grinding glass and ceramics. Many fine cutting edge particles are formed due to small fragmentation before the polycrystalline particles break out from the binder during grinding. Therefore, the abrasive particles can be better utilized in hard metal grinding.
Particle size
The particle size is equivalent to the number of meshes that can be passed through exactly one inch of the screen before the next screen, which is more densely meshed. Very fine particles can be separated by panning. The grain size of diamond and boron nitride is equivalent to the width of UM mesh. The grain size of the D150 (diamond abrasive) or B150 polycrystalline cubic boron nitride (CBN) abrasive ranges from 125 to 150/um. The higher the required surface roughness of the workpiece, the sharper the edge of the grinding profile, and the finer the abrasive particle size must be.
Bond
The purpose of the bond is to hold the individual abrasive particles together for a long time until they are blunt. The grinding wheel with ceramic bond has pore space, so it has good dressing ability. Artificial resin bond can bond particles more firmly and therefore can withstand greater grinding forces. However, the arbitrary arrangement of the grain tips can produce a lower temperature grinding.
Hardness of abrasive tools
The hardness of grinding wheel should not be understood as the hardness of abrasive particles, but as the resistance of adhesive to prevent abrasive particles from disengagement. In the grinding of hard materials, jimi rub wear is large and grinding load is small, so only the soft grinding wheel can produce "self-sharpening effect". When grinding soft materials, thicker chips require larger grain retention, so a harder wheel is required. A soft grinding wheel is always uneconomical from the point of view of processing cost due to its high wear: the abrasive particles detach from the grinding wheel disc before the wear surface is formed, and the grinding wheel quickly loses its shape (contour), that is, the grinding wheel "collapses". On the contrary, a hard grinding wheel keeps the grain too long, and the grinding wheel "lubricates" and grinds. At the same time, the grinding pressure and temperature in the contact area between the grinding wheel and the parts also rise. The effective hardness of grinding wheel depends not only on the hardness of abrasive material, but also on the particle size, pore volume and chip thickness before leaving the workpiece.
For hard workpiece materials, a soft grinding wheel should be selected, and for soft workpiece materials, a hard grinding wheel should be selected. For thin chip cutting with fine abrasive particles, a softer grinding wheel should be used because the abrasive particles of this grinding wheel are easier to detach due to the greater effective hardness.
Balance of grinding wheel
The uneven distribution of abrasive particles and adhesives will lead to centrifugal force due to the unbalance of the grinding wheel disk.
Therefore, for large and wide grinding wheels, especially those with high circumferential speed, the balance of grinding wheel disc is particularly important.
For static balancing, place the grinding wheel on a balance scale or balance rolling frame.
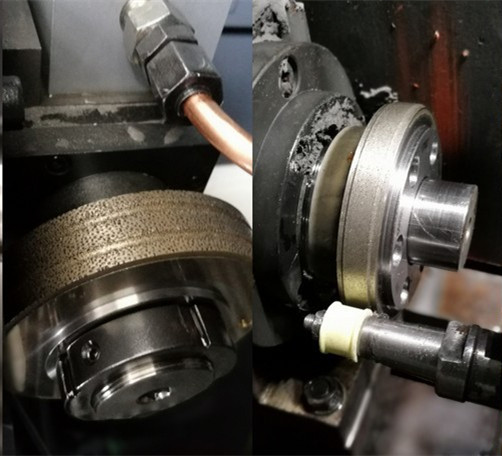
Dressing of grinding wheel
• Trim the shape
Make the grinding wheel disk contour, radius and size are kept within the tolerance range. The radial and axial runout performance of the newly clamped grinding wheel must be improved.
• Sharpening
The volume of the chip storage chamber is expanded by grinding the binder, and the cutting performance of the grinding tool is improved. The natural corundum grinding wheel and silicon carbide grinding wheel can achieve sufficient sharpness after shaping and dressing of diamond or steel dressing grinding wheel. While diamond grinding wheel or polycrystalline cubic boron nitride (CBN) grinding wheel must be shaped by silicon carbide dressing wheel or diamond dressing grinding wheel. When sharpening, the natural corundum grindstone shall be used to remove the bonding agent until the outstanding state of the abrasive particle reaches 1/3 of its particle size.
Safety precautions for grinding
The grinding wheel disc using ceramic binder is a type of easily cracked grinding wheel. If the grinding wheel is cracked due to hairlike cracks or incorrect fastening, when the circumferal speed of the grinding wheel reaches 80m/s (equivalent to 288km/h), there is a risk that the grinding wheel fragments will fly out and cause death. Only on the premise of strictly obeying the safety rules, grinding is a safe machining method.
Welcome to contact us:
Email:info@moresuperhard.com